 You have a chipped tooth, cracked tooth, fractured tooth, broken tooth, displaced or knocked out tooth. What do you do?
You have a chipped tooth, cracked tooth, fractured tooth, broken tooth, displaced or knocked out tooth. What do you do?
First, How Serious is the Injury?
Trauma to the face may result in an injury as slight as a small chipping of tooth enamel (the outermost layer of a tooth) to one as severe as completely knocking a tooth out of it’s socket and/or fracturing the jawbone(s).
If your broken, fractured, chipped or cracked tooth is the result of trauma to your head or face and it is accompanied by bleeding from the nose or ears, loss of memory or consciousness, dizziness, disorientation, severe head or ear ache or if your teeth do not fit together properly after the trauma, go to a hospital emergency room for evaluation immediately. You may have injured your brain, caused bleeding inside of your skull, broken your TMJ (jaw joint), jawbone or other bones of your face. For this you will need immediate, emergency medical care. Most hospitals have an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon available to diagnose and treat your injuries in addition to emergency room physicians.
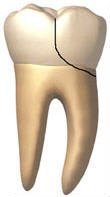
Fortunately, most injuries are much less severe. Broken teeth – chipped teeth, fractured teeth, cracked teeth – and loosened or knocked out teeth are classified into the following basic types (listed in order of severity):
- Crown Fractures (The part of the tooth above the gumline)
- Enamel
- Craze Line(s) – Cracked enamel without loss of tooth structure
- Chipped Tooth – Cracked and fractured enamel involving loss of this outermost layer of tooth structure
- Enamel and Dentin – Fracture and exposure of the outer and middle layers
- Enamel, Dentin and Pulp – Fracture and exposure of the outer, middle and inner layers
- Enamel
- Root Fractures (The part of the tooth below the gumline)
- Horizontal – A horizontal crack in the tooth root
- Vertical – a vertical crack in the tooth root
- Displaced or loosened teeth within the tooth socket (Where the tooth sits inside your jaw)
- Concussion – The tooth has absorbed the force of the injury
- Displacement – The tooth has become dislocated in it’s socket
- Avulsion – The tooth has been released from it’s socket
Contact Bravo Dental. Our Miami dentist can assess the type of injury and perform a complete oral examination as well as the appropriate treatment plan for your condition.
